Coxarthrosis.- This is a chronic degenerative disease, leading to bone tissue deformation.With Coksartrosis, all ingredients of the joints are related to the pathological process: articular cartilage, bone structure adjacent to cartilage, epidemic shell, ligament, cyst and nearby muscle.In the case of disease, articular cartilage is destroyed, the redimits of bones and bones (bone growth) appear, and the inflammation of the mechanical binding apparatus of the hip joint occurs.
In the world, each of the fifth complains about joint issues with joints.This may be both pain or restricting movement in joints, and the combination of these symptoms.Each second outpatient vision falls into patients with musculoskeletal disorders, while 66 % of cases are people under 65 years old.According to the latest epidemiological research, the incidence of knee and hip joints in the adult population is 13 %.
Risk factors for the development of COXARTHROSIS:
- Genetic trend.A common cause of Coksartrosis of hip joints is congenital or obtained mutations of type II ProLagen.
- Age.The possible cause of the popularity of arthritis in old age is the difference between the effect of damaging the articular cartilage of the external environment and the ability to recover.
- Floor.Women with osteoarthritis more often than men.This is due to the influence of the effect of estrogen female sex hormones on bone metabolism.However, the influence of the floor is vague - according to some authors, unlike the damage to other joints, there is no difference in the sexual basis for Cocksartrosis: In men, the joints of the hip joint are often found as in women.
- Excess body weight.The relationship is proven between excess body mass and the appearance of arthritis.Excess adhesive tissue increases the load harmful to cartilage.In addition, adipose tissue produces Pro -inFlammat enzymes that damage cartilage tissue.
- Regular development of bones and joints.According to studies, 80 % of Coxarthrosis, there is no clear reason, related to previous defects that have been diagnosed before the development of hip -dysplasia and subluxation.
- Heavy physical labor.An excess load on the hip joints with some types of physical labor can lead to damage to joints and the formation of muscle disease.There is a risk of agricultural workers, miners and people with similar specialties.
- Injury.The risk of developing COXARTHROSIS increases after hip joint injury.Moreover, both injured joints and both can participate in this process.
- Professional sports.Professional sports can cause the appearance of Coxarthrosis both because of over -loading on joints and injuries.Dangerous sports are likely to include heavy athletics, athletics, and skydiving sports.
- Bone and joint disease- Rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis arthritis, joint infection, vascular necrosis, gouty arthritis, etc.
- Endocrine pathology- Hypothyroidism, Hypoparathhyroidism, Acromegaly (weakened pituitary function), diabetes, obesity.
If the same symptoms are detected, consult a doctor.Do not give yourself - it's dangerous for your health!
Symptoms of hip joint disease
The main symptoms of COXARTHROSIS include: pain, movement and crunchy in joints, their deformation, shortening the function of the lower limbs and periodic swelling in the joints.
Pain of different intensity.The pain in the joint is negligible and arise in a short time.They appear or strengthen while walking or with other physical efforts, for example, during squatting, tilting and lifting weights.As the disease develops, the pain increases and even resting for a long time does not bring relief.In addition, pain occurs with prolonged immobility and joint fixation in a position.
The patient complained about the "starting" pain in the hip after sleeping, driving in a car and another prolonged immobilization."Starting" pain for Coxarthrosis lasts no more than 30 minutes.Pain increases during body temperature or in a stressful situation.They can be localized in the area of the buttocks or groin, on the front or side of the thigh.With the spread of the pain on the nerves of the lumbar plexus, it can be transmitted to the distance from the center of the body or at the knee.Sometimes the pain applies to lumbar spine and spine.
General mobile restriction.Movement in the hip joint with Coksartrosis is limited due to pain.At the same time, rotating (rotating both inside and outside) and giving the lower limb (moving to the middle of the body) is often more disturbed, but may be limited (moving from the middle axis of the body), as well as bending and expanding.The inability to perform passive movements in the joints due to a clear pain syndrome causing the pelvic bias.The patient's gain changes, the buttocks are sticky, the body goes forward before changing the weight to the damaged side.With the damage of both sides in patients with Coksartrosis, a "duck gait" was formed.
With periodic coxarthrosis occursswelling in the jointCan be invisible due to muscle and fat layer.In addition, this disease is characteristicCrystals in joints during motion, gradual deformation and shorten the function of the lower limb.
Usually, a joint is affected by the disease, then the process is applied to others.But sometimes arthritis affects some joints at the same time and polyosostoartherther inflammation occurs.Polyosteoarthrosis is characteristic of the elderly or tends to be inherited and simultaneously - bone, joint and endocrine disorders.
Pathogens of hip joints
In the pathology of arthritis, an important role is played by mechanical lesions (trauma and microtraumas due to strengthening physical strength on joints) and genetic, hormonal and metabolic factors.Normally, any factors have not been able to affect the development of the disease in a specific patient, but often the disease develops after tissue damage to mechanical lesions.
Damage to tissue stimulates the division of cartilage tissue cells (chondrocytes), while the production of cytokines Pro -inflangmatization increases, usually in cartilage in small quantities.Cytokines start the inflammatory process, for example, under the influence of cytokine Il-1 causing inflammation, enzymes are distinguished from destroying cartilage of joints.In addition, under the influence of cytokine, the production of TSOG-2 enzymes and other substances has a toxic effect on increased cartilage.
Synovites also plays a big role in the development of Coxarthrosis - inflammatory diseases of synovial shells of joints or ligaments with the accumulation of liquids in the compartment.
The decrease in the elasticity and the power of articular cartilage associated with metabolic disorders lead to reduced its mechanical stress resistance.With Coksartrosis, all components of joints are related to pathological processes, including epidural bones.Due to the fact that the large joints of the lower limbs occupy the large joints of the body, they have significant mechanical stress, so the microfinance occurs in the lower sheet sheet and cartilage.As a result of the microvelomas, the subtractor bone is compressed, leading to the development of the area of bone tissue - osteoporosis.And this, in turn, stimulates further degradation of articular cartilage.
In some cases, the joint of the hip is inherited.Genetic joint disease is said to be genetic genetic - due to the effects of many genes, each gene affected weakly.The cause of some diseases is the gene mutation that encodes the molecules of articular cartilage, causing its rupture.The genes are responsible for the division of the chondrocytes may also be affected.In addition, metabolic disorders are inherited, such as pyrophosphate joints - a disease in which the Calcium Pyrophosphate crystals accumulate in articular cartilage and fluid fluid.
Classification and development stages of joint disease of hip joints
Depending on the cause of the disease, Coxarthrosis is divided into two main forms: Nguyen Phat (idiopathic) and secondary (arising from or for other diseases).
Main Coksartrosis:
- Local (only affecting hip joints):
- unilateral;
- bilateral.
- General (polyosteoarthrosis) with a lesions of at least three joints (for example, hips, knees and small joints of the brush or foot).
Secondary arthritis:
- Post -Traumatic:
- Acute - as a result of acute injury;
- Chronic - due to classes of some sports or as a result of professional activity.
- Metabolic disease (Oconosis, hemochromatosis, Wilson disease, Gaucher).
- Congenital disease and development defect (congenital dysplasia of hip joints, pertes disease, Epiphyse sliding of the femur, hypermobility syndrome, shortening of lower limbs, scoliosis, bone dysplasia).
- Endocrine diseases (Acromegaly, hypothyroidism, diabetes, hyperthyroidism, obesity).
- Calcium salts (pyrophosphate joint disease, calcification tendonitis).
- Bone and joint disease (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis arthritis, Pedhetic disease, infections, infection).
According to clinical manifestations, the following forms of coxarthrosis are distinguished:
- Less symptoms.
- Manifestations, manifestations by clinical symptoms:
- Quickly progress, in which symptoms developed in the first four years from the beginning of the disease;
- Slow progress - Clinical symptoms appear after five years of the disease.
According to the image x -ray, two types of joints can be determined:
- Agency - With signs of increased recovery reaction (lesions are replaced by a new tissue, for example, osteoporosis appears);
- Atrophy (reduce tissue volume).
The stages of the disease can be determined in terms of radioactive and clinical.To determine the X -ray stage of hip arthritis, the classification of Kellgren and Lawrence (1957) is most commonly used.
The stages of arthritis in the classification of X -ray
| Stage | Token |
|---|---|
| 0 | There is no sign of arthritis in X -Ray images |
| 1 | The general distance does not change, the only area bone cells are visualized |
| 2 | The general distance has not changed, the important bone cells are visualized |
| 3 | The height of the moderate decrease of joint distance, the regional bone cells are significantly visualized |
| 4 | The height of the gap is significantly reduced, the bone cells in the area are significantly and the epidural joint disease is visualized (compressing the bone tissue under the surface of the cartilage lower than the structure of cartilage) |
To determine the clinical stage of the disease, the classification (1961) is used, using both clinical signs and visual criteria.
The clinical stage of arthritis
| Stage | Token |
|---|---|
| 0 | The joint distance is decisively and unevenly narrowed, the edges of the cracks are indicated a bit |
| 1 | The joint distance is significantly narrowed (50-60 %), significant bone cells, healing under epidural and enlightenment in bone Epiphees;The clinic dominates by the moving restriction in the joints, a rough crisis in movements, not significant or moderate muscle atrophy. |
| 2 | deformation, stiffness of joints;The joint distance is narrowed more than 60-70 % of the rated or completely absent, bone cells, cysts under the epidural |
Complications of the joints of the hip joint
With Coxarthrosis, all complications are accurate with pathological changes in joints.
The Coksartrosis process may be complicated by local inflammatory processes:
- Busite - Angelitis in the joints;
- Tendonitis - inflammation of the inner shell of the vagina of the muscle tendon;
- The tunnel syndrome of the nerve is due to the formation of large bone cells or with joint deformation.
With the progression of COXARTHROSIS and its conversion to the clinical stage II and III, the pain limits the movement of joints, and over time, ankylosis (fibroids, bones or cartilage) occurs, accompanied by its complete immobility.
Significant joint deformation can lead toFracture or sterile necrosis of the bone.For Coksartrosis, the sterile necrosis of the femur is the most formidable complication.
With a clear Coksartrosis disease, may occursublimation and dislocationsAs well as the penetration of the femur into the pelvis.The deviation and sublimation of the hip leads to pain (at first acute, then dull and painful), enhanced while walking and struggling, as well as deformed joints, lame and sometimes shortened limbs affected.
Despite the lack of systemic system manifestations, in modern clinical practice, more attention to diseases related to it.These are pathological conditions that exist or arise on the basis of the current disease.Regarding inflammatory reactions arising during joints, the formation of atherosclerosis on the inner walls of the ships is enhanced, increasing the riskCardiovascular disease.Reducing physical activity due to pain and limiting the movement of joints leading toObesity, depression and decline in quality of life.With the extended use of anti -inflammatory drugs not due toThe above gastrointestinal tract parts are affected,And the sameThe risk of cardiovascular disease and kidney disease increases.
Diagnosis of hip joint disease
The diagnosis of "Coksartrosis" is performed on the basis of clinical manifestations and X -ray examination.There is no sign of typical laboratory to diagnose muscle disease.
Among the clinical manifestationsIt is to diagnose the joints of the hip joints that is pain and its characteristics.Pain for joint disease occurs and gradually develops for several years (sometimes a few months with rapid progression).The pain occurs or strengthens during exertion or standing position.If the patient starts to feel pain alone, then inflammation (epidemic inflammation) has participated.The statement is recorded by 30 minutes in the morning and with prolonged immobility.
The limitations of the general mobility are increasing, this applies to both operating and passive movements.With the development of the disease, the joints are deformed, the shortening of the function of the limb length may occur.
In a physical testThere is a limit of the ability to move joints, deform them, shorten limbs, pain when touching the joints and a large rotation of the femur, muscle atrophy.
Laboratory methodThere is no need to diagnose the joints of the hip joint.However, they can be used to distinguish Coxarthrosis with arthritis (rheumatism and chronic), because with Arthrosis has no changes in inflammation in the overall blood test and rheumatism, and uric acid levels do not increase.In addition, using laboratory tests, contraindications are disclosed for drug treatments.
Tool methodTo diagnose the joints of the hip joint:
- X -ray- This is the main method to diagnose the joints of the hip joints.X -ray identifies the characteristic changes of Coksartrosis: narrowing the gap of joints, osteoporosis, erosion and ulcers of cartilage, cystic cysts under endominity and sclerosis.X -Ray test is a classic method to diagnose Coxarthrosis and X -ray signs as a basis for the classification of COXARTHROSIS.However, at present, other visualization methods of joints are increasingly used, such as magnetic resonance images and ultrasound.
- Ultrasonic test (ultrasound) -The advantage of ultrasound is that in the absence of a piercing load on the body.
- Magnetic resonance layer (MRI)- Compared to other methods, it allows you to better visualize joint damage.
- Endoscopy joints-Allows you to identify damage to articular cartilage: from chondromation areas (softening articular cartilage) with diameter of less than 10 mm to deep cracks penetrate the lower bone and the formation of deep ulcers.The outer and medium cracks and surface erosion can also be visualized.
The identification of Coksartrosis usually does not represent special difficulties, but when assessing a specific clinical situation, it is necessary to remember the possible secondary source of the hip joint (for example, complications of other diseases, for example, with endocrine disorders).
Treatment of arthritis of hip joints
Treatment of hip joints may be conservative (drugs and not infected) or active.Conservation treatment is used in 1-2 stages of the disease, 3-stage surgery.Surgical treatment can be recommended in two stages with persistent pain and lack of reactions to conservative therapy.
Objectives of conservative therapy:
- Improve life quality - relieve pain and increase general mobility;
- Stop or slow down the development of the disease.
The treatment does not include:
- unloading hip joints (reducing body weight, creating additional support and conversion of body weight to sugarcane or crutches);
- Physiotherapy physical therapy;
- Physical therapy treatment.
Coxarthrosis treatment begins with methods that are not an important role assigned to physical therapy exercises.With intense pain, patients should use support.With a clear disease and the presence of contraindications to Endoprosthetic, the support must be used for life.
Coxartrosis treatment therapyIncluding drugs that reduce the symptoms of the disease.These are painkillers, as well as non -anti -inflammatory drugs (NSAID).The NSAIDs are divided into unchanged and selected.
Analgesics and NSAID for joints of the hip joints are used for a short time to relieve pain and inflammation.Currently, there is no proven advantage of an anti -inflammatory agent is not another substance, so choosing a specific drug depends on side effects and a specific clinical situation caused by it.
Remember that NSAID has some side effects.When using them, the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum is affected, because it may have ulcers and bleeding.Some NSAIDs have toxic effects on the liver and kidneys.In addition, NSAID disrupts platelets, and therefore, the patient is broken down by thrombosis and tends to bleed.NSAIDs with prolonged use to prevent hematopoietic processes and can cause proliferate anemia and Agranulocytosis.Selective NSAID receives significantly less complications.
Ointment and gel are used local causing less side effects than oral products.To treat muscle diseases, drugs with heating and pain relief are used.They can contain pine, yeast, nicotinic acid esters, salicylate, bee venom.In addition, NSAID works well.
In the absence of painkillers and NSAIDs or if it is not possible to choose the optimal dose of the drug, the painkiller of the central action may be prescribed short -term.
In the case of inflammation, the use of internal corticosteroids is used.Corticosteroids are used no more than 2-3 times a year, because more often can lead to cartilage degeneration.
The drug has a slow impact that weakens the symptoms of the disease including Chondroprotector, the inappropriate compounds of butter or soy, hyaluronic acid.These drugs are included in the recommendations of the anti -European Union for the treatment of joints of the hip joint.Prepare pain relief and improve general motor ability.
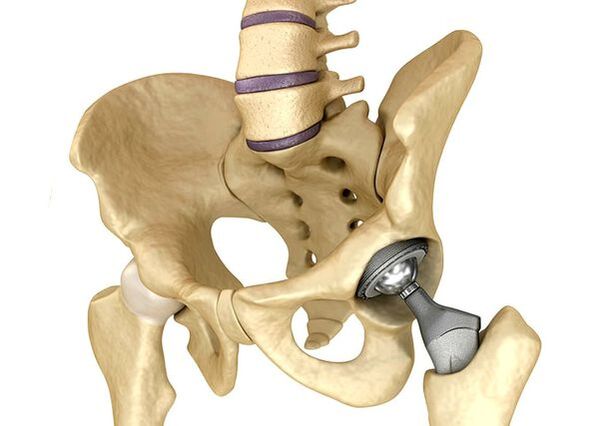
Endoprosthetic of the hip jointIt is used in serious cases of phase III, when the pain syndrome cannot be removed and the mobility of the joint is significantly limited.The prosthetic leg of the hip leads to a decrease in pain syndrome, an improvement in the function of joints and the quality of life of the patient.Effectiveness still exists for 10-15 years, then may need a second activity.During surgery, the hip joint is replaced by imitation of artificial and metal artificial artificial imitations (often used for fake titanium parts) or polymer.
Forecast.Prevent
The prognosis of arthritis of the hip joints related to the life of the patient is favorable, but the disease often leads to defects.According to the World Health Organization, 80 % of elderly patients with Coxarthrosis have violated mobility and 25 % cannot do daily problems.In this regard, the main prevention of the hip joint is very important.
Preventive measures:

- Reduce body weight.It is necessary to adjust nutrition to reduce weight and load on joints.In addition, the decrease in the volume of fat tissue reduces the amount of intermediate inflammatory substance that it releases.
- Avoid heavy physical labor and sports overload.Physical overload is often the cause of the joints of the hip joints, while moderate physical activity, on the contrary, improves the condition of articular cartilage, retains the ability to exercise normally and reduce the load on other joints.
- Basic medical repair.If the patient is discovered in diseases that can lead to secondary Coksartrosis (endocrine, rheumatism and others), hidden disease is necessary.The normalization of hormonal platforms and the achievement of persistent remission of rheumatism is the prevention of the main arthritis, and allows you to slow down its development.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.A balanced diet with enough plant and animal protein, non -saturated fatty acids and simple carbohydrates, as well as moderate physical activity, avoiding the appearance of COXARTHROSIS even when there is risk factors.
Currently, the prevention of hip joint diseases is mandatory in newborns and pediatrics.Over time, congenital dysplasia is regulated by the hip joint significantly reduces the risk of Coxarthrosis in adulthood.

























